
Advances in toughened polymer materials by structured rubber particles.
Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2022, 139

Polymer BEPCSR system may be related to the fact that CSR has a relatively 2006 47 (22):77119. In this study, a CSR, pre-dispersed, diglycidyl epoxy of. The lower weight residue observed with the nanocomposites: preparation, characterization and properties. Core-shell rubber (CSR) nanoparticles are known to enhance the toughness of epoxy systems.
#Core shell rubber series#
Effect of polypropylene molecular weight distribution on the balance between the toughness and rigidity of the impact polypropylene composites. Multiwalled carbon nanotube/polybenzoxazine 24.8, respectively. Essentially all the literature reviewed in the preceding paragraph emphasized identification rather than control of rubber-phase distribution.Recently, our laboratory conducted a series of investigations to identify and control rubber-phase distribution in several binary blends by using functionalized core-shell rubber. Fushi Li, Yunbao Gao, Nan Yan, Chunyu Zhang, Xuequan Zhang, Wei Jiang.
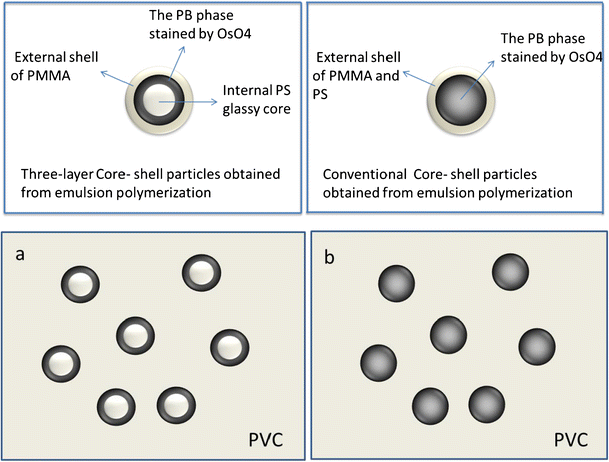
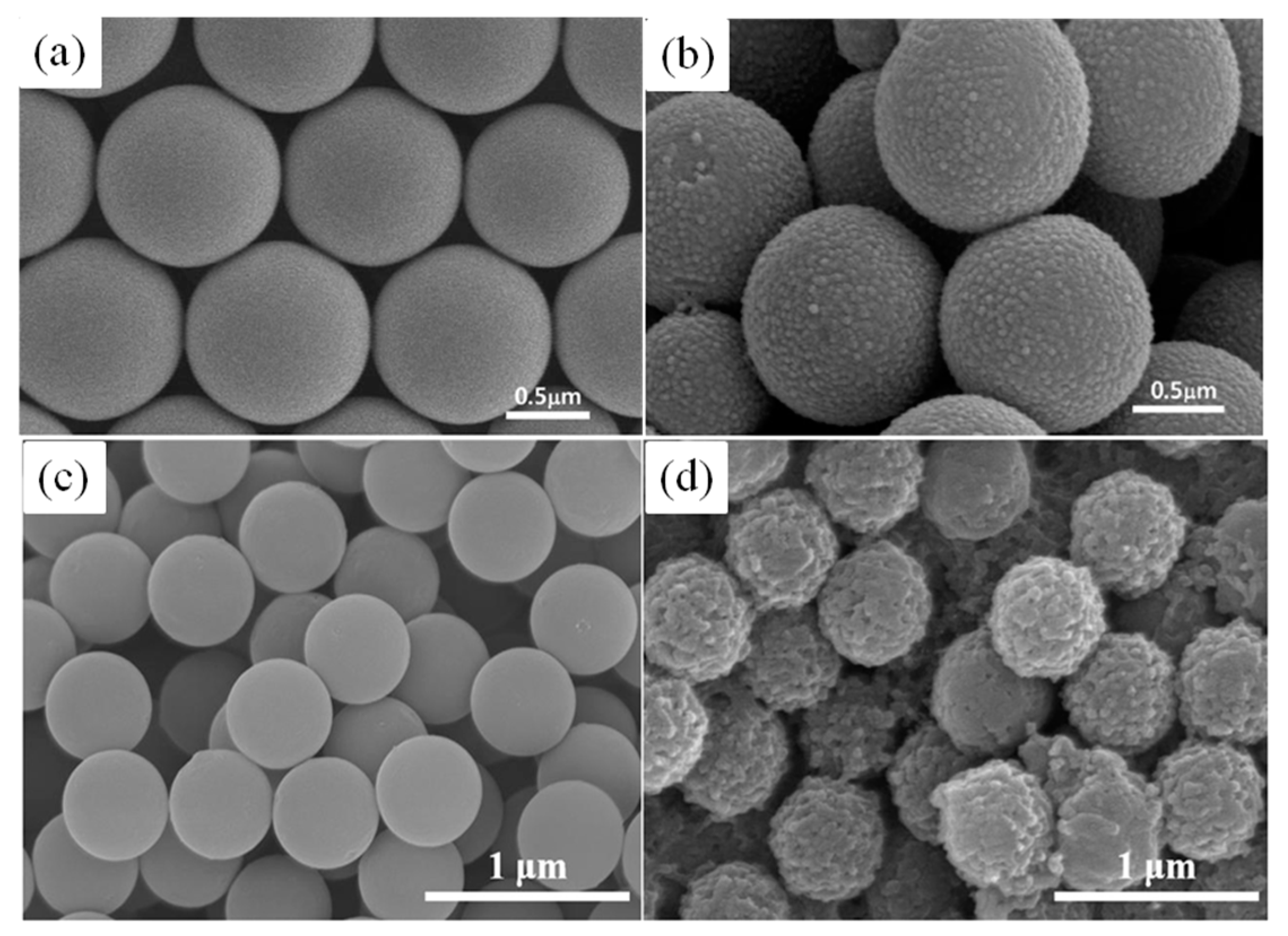
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2013, 52 Effect of Entanglement Density on Mechanical Properties and Deformation Behavior of Rubber-Modified PVC/α-MSAN Blends. Lixin Song, Liang Ren, Mingyao Zhang, Sulin Sun, Guanghui Gao, Yu Gui, Lixia Zhang, and Huixuan Zhang.Moreover, the stress whitening zones were observed by transmission electron microscopy, and the result showed that multiple crazing is its dominative toughening mechanism. Co-Polymer II designed to be compatible with thermosetting resin. When the rubber particle size was above 300 nm, the notched impact strength was 208 J/m, nearly 2 times than that of toughened PS with particle size 100 nm. What is Core-Shell Rubber (CSR) 2-Layer CSR. From measuring mechanical properties, it was found that the notched impact strength of toughened PS was significantly influenced by core–shell PB- g-PS particle size.

Then the submicrometer sized PB- g-PS impact modifiers were utilized to toughen polystyrene (PS) by blending PS and high-impact polystyrene. Subsequently, core–shell polybutadiene- graft-polystyrene (PB- g-PS) particles were synthesized using a redox initiator system (cumene hydroperoxide and ferrous sulfate) by an emulsion grafting polymerization. These improved results confirm that although the decrease of tensile modulus cannot be avoided with increasing impact strength, increasing the elastic modulus and yield strength of the core material in the rigid core/soft rubber shell toughener is an effective way to obtain a good balance of elastic modulus, tensile yield strength and impact strength.A series of submicrometer-sized polybutadiene (PB) rubber particles with different diameters ranging from 100 to 450 nm were prepared via an emulsion polymerization. When this core/shell toughener containing 5 wt% PB- g-MAH is blended with PA6 in the weight ratios of 10/90 and 30/70, the Izod impact strengths are 390 and 480 J m −1 (which are 330 and 550% increases compared to neat PA6), and the modulus are 2.37 and 2.13 GPa, and yield strength are 60.2 and 54 MPa, respectively (which represent only 6 and 15% loss of modulus, and 5 and 13% decrease in yield strength relative to neat PA6). In this study, we have redressed this problem by replacing the LDPE core with a polypropylene (PP) core, which has both higher elastic modulus and yield strength than that of LDPE, forming a new core/shell (PP/PB- g-MAH) toughener. However, this is at the expense of quite large losses in elastic modulus of 10–25% and tensile yield strength of 30–55%, especially at high core/shell rubber loading ( e.g., 30 wt%). We have recently shown that by adding 10 to 30 wt% core/shell toughener with a low density polyethylene (LDPE) core and a polybutadiene- g-maleic anhydride (PB- g-MAH) rubber shell to polyamide 6 (PA6), the impact strength of PA6 matrix can be significantly increased by 600–1000%.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
